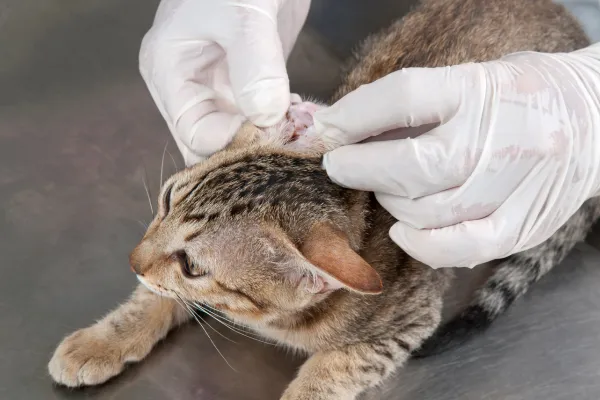
Common Pet Ailments in Northern BC: Ear Infections
Common Pet Ailments in Northern BC
Part Two: Ear Infections in Pets
Ear infections, medically termed otitis externa, are a prevalent health concern among pets in Northern British Columbia. These infections involve inflammation of the external ear canal and can cause significant discomfort if left untreated. Understanding the specific causes, effective treatments, and preventive strategies is essential for maintaining your pet's ear health.

Common Causes of Ear Infections in Northern BC
Bacterial and Yeast Infections:
Cause: The primary culprits behind ear infections in dogs are bacteria and yeast. Factors such as moisture accumulation, allergies, or foreign bodies can create an environment conducive to the overgrowth of these microorganisms.
Remedy: Veterinary intervention is necessary to determine the specific pathogen involved. Treatment typically includes thorough ear cleaning followed by the application of appropriate topical medications, such as antibiotics or antifungals. In more severe cases, systemic medications may be prescribed.
Allergies:
Cause: Allergic reactions to environmental factors or certain foods can lead to inflammation of the ear canal, making pets more susceptible to infections. Studies indicate that ear infections occur in 65-80% of dogs with underlying food allergies.
Remedy: Identifying and managing the underlying allergy is crucial. This may involve dietary adjustments, environmental modifications, and the use of medications to control allergic responses.
Ear Mites:
Cause: Ear mites are highly contagious parasites that can infest the ear canal, leading to irritation and infection. They are a common cause of ear infections in cats and can also affect dogs.
Remedy: Treatment involves the application of veterinarian-prescribed antiparasitic medications to eliminate the mites. All pets in the household should be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfestation.
Foreign Bodies and Trauma:
Cause: Objects like grass seeds or debris can become lodged in the ear canal, causing irritation and subsequent infection. Additionally, excessive ear cleaning or rough handling can lead to trauma and inflammation.
Remedy: A veterinarian can safely remove foreign objects and provide appropriate treatment to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. It's important to handle your pet's ears gently and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal during cleaning.
Anatomical Factors:
Cause: Breeds with floppy ears or excessive hair in the ear canal are more prone to infections due to reduced air circulation and increased moisture retention.
Remedy: Regular grooming to remove excess hair and routine ear inspections can help mitigate this risk. In some cases, surgical intervention may be considered to improve ear canal ventilation.

Treatments and Remedies
Professional Ear Cleaning: A veterinarian will perform a thorough cleaning to remove debris, wax, and infectious agents from the ear canal. This process is essential for the effectiveness of subsequent treatments.
Topical Medications: Depending on the infection's cause, topical treatments may include antibiotics, antifungals, or anti-inflammatory drugs. For instance, medications containing gentamicin, betamethasone valerate, and clotrimazole are commonly used to address bacterial and fungal infections.
Systemic Medications: In cases of severe or chronic infections, oral or injectable antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to address deeper infections and alleviate systemic symptoms.
Surgical Intervention: For chronic, recurrent infections unresponsive to medical management, surgical options such as a total ear canal ablation may be considered to provide long-term relief.
Preventive Measures
Regular Ear Inspections: Routinely check your pet's ears for signs of redness, swelling, or unusual discharge. Early detection of abnormalities can prevent the progression of infections.
Proper Ear Cleaning: Clean your pet's ears as recommended by your veterinarian, using appropriate solutions and techniques. Avoid over-cleaning, which can lead to irritation.
Allergy Management: Work with your veterinarian to identify and manage any underlying allergies that may predispose your pet to ear infections. This may involve dietary changes or environmental modifications.
Moisture Control: After swimming or bathing, ensure your pet's ears are thoroughly dried to prevent moisture buildup, which can create an environment conducive to infection.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule routine examinations to monitor your pet's overall health and promptly address any emerging ear issues.
Ospika’s Treatment Approach
Examinations and Swabs: To determine the cause of irritation and possibly infection; bacterial or fungal.
Topical Treatments: Antibiotics, antifungals, and anti-inflammatories.
Systemic Medications: For deeper or chronic infections.
Surgical Options: For severe, unmanageable infections.
At Ospika Animal Hospital in Prince George, BC, our experienced veterinary team is adept at diagnosing and treating ear infections in pets. We provide comprehensive care tailored to the unique needs of your animal companions. If your pet is exhibiting signs of an ear infection, such as head shaking, scratching, or unusual discharge, contact Ospika Animal Hospital for expert evaluation and treatment. We use advanced diagnostic tools and years of experience to manage ear infections swiftly and effectively. Trust our compassionate team to help your pet heal.
